Description:
Our neural network-based translation service offers a user-friendly interface, allowing you to access expertly trained Transformer models with ease.
Description:
A neural networks based translation service provides a simple UI and API that lets you use Transformer models trained by our experts. Five models are currently provided with more to come.
Description:
UDPipe is an trainable pipeline for tokenization, tagging, lemmatization and dependency parsing of CoNLL-U files. UDPipe is language-agnostic and can be trained given only annotated data in CoNLL-U format. Trained models are provided for nearly all UD treebanks. UDPipe is available as a binary, as a library for C++, Python, Perl, Java, C#, and as a web service.
UDPipe is a free software under Mozilla Public License 2.0 and the linguistic models are free for non-commercial use and distributed under CC BY-NC-SA license, although for some models the original data used to create the model may impose additional licensing conditions.
Description:
NameTag is an open-source tool for named entity recognition (NER). NameTag identifies proper names in text and classifies them into predefined categories, such as names of persons, locations, organizations, etc. NameTag is distributed as a standalone tool or a library, along with trained linguistic models. In the Czech language, NameTag achieves state-of-the-art performance (Straková et. al. 2013). NameTag is a free software under LGPL license and the linguistic models are free for non-commercial use and distributed under CC BY-NC-SA license, although for some models the original data used to create the model may impose additional licensing conditions.
Description:
MorphoDiTa: Morphological Dictionary and Tagger is an open-source tool for morphological analysis of natural language texts. It performs morphological analysis, morphological generation, tagging and tokenization and is distributed as a standalone tool or a library, along with trained linguistic models. In the Czech language, MorphoDiTa achieves state-of-the-art results with a throughput around 10-200K words per second. MorphoDiTa is a free software under LGPL license and the linguistic models are free for non-commercial use and distributed under CC BY-NC-SA license, although for some models the original data used to create the model may impose additional licensing conditions.
Description:
Treex (formerly TectoMT) is a highly modular NLP software system implemented in Perl programming language under Linux.
It is primarily aimed at Machine Translation, making use of the ideas and technology created during the Prague Dependency Treebank project. At the same time, it is also hoped to significantly facilitate and accelerate development of software solutions of many other NLP tasks, especially due to re-usability of the numerous integrated processing modules (called blocks), which are equipped with uniform object-oriented interfaces.
Description:
The system Česílko was designed as a tool enabling the fast and efficient translation from one source language into many target languages, which are mutually related. The system receives as its input a high quality human translation of the original into Czech (from any language). It translates the Czech input into a number of languages related to Czech. The system contains at the moment 5 language pairs, 4 of them only as experiments, namely Czech into Polish, Lithuanian, Macedonian and Lower Sorbian. Unfortunately, the system cannot be tested on arbitrary texts for these language pairs due to a small size of all dictionaries. The only working language pair (and at the same time also exploitable outside of the above mentioned setup) is the fifth one, Czech to Slovak. Similarly to other MT systems, Česílko requires human post-editing. The system is being developed since 1998
Description:
PML-TQ is a powerful open-source search tool for all kinds of linguistically annotated tree-banks with several client interfaces and two search back-ends (one based on a SQL database and one based on Perl and the TrEd toolkit). The tool works natively with tree-banks encoded in the PML data format (conversion scripts are available for many established tree-bank formats).
Description:
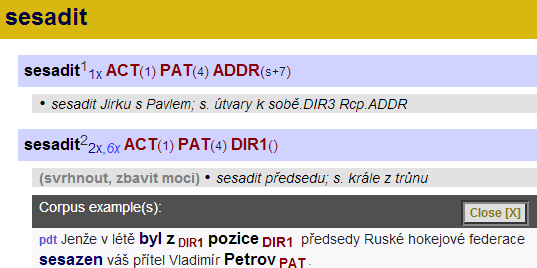
The valency lexicon PDT-Vallex has been built in close connection with the annotation of the Prague Dependency Treebank project (PDT) and its successors (mainly the Prague Czech-English Dependency Treebank project, PCEDT). It contains over 11000 valency frames for more than 7000 verbs which occurred in the PDT or PCEDT. It is available in electronically processable format (XML) together with the aforementioned treebanks (to be viewed and edited by TrEd, the PDT/PCEDT main annotation tool), and also in more human readable form including corpus examples (see the WEBSITE link below). The main feature of the lexicon is its linking to the annotated corpora - each occurrence of each verb is linked to the appropriate valency frame with additional (generalized) information about its usage and surface morphosyntactic form alternatives.
Description:
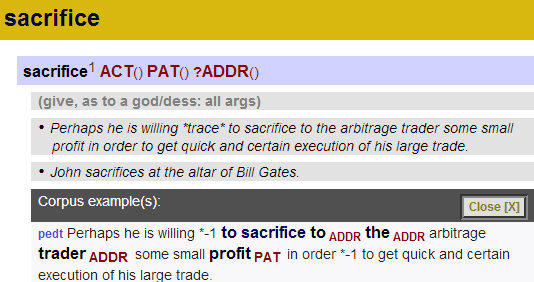
EngVallex is the English counterpart of the PDT-Vallex valency lexicon, using the same view of valency, valency frames and the description of a surface form of verbal arguments. EngVallex contains links also to PropBank and Verbnet, two existing English predicate-argument lexicons used, i.a., for the PropBank project. The EngVallex lexicon is fully linked to the English side of the PCEDT parallel treebank, which is in fact the PTB re-annotated using the Prague Dependency Treebank style of annotation. The EngVallex is available in an XML format in our repository, and also in a searchable form (see the WEBSITE link below) with examples from the PCEDT.
Description:
CzEngVallex is a bilingual valency lexicon of corresponding Czech and English verbs. It connects 20835 aligned valency frame pairs (verb senses) which are translations of each other, aligning their arguments as well. The CzEngVallex serves as a powerful, real-text-based database of frame-to-frame and subsequently argument-to-argument pairs and can be used for example for machine translation applications. It uses the data from the Prague Czech-English Dependency Treebank project (PCEDT 2.0) and it also takes advantage of two existing valency lexicons: PDT-Vallex for Czech and EngVallex for English, using the same view of valency (based on the Functional Generative Description theory). The CzEngVallex is available in an XML format in the LINDAT/CLARIN repository, and also in a searchable form (see the “More Apps” tab) interlinked with PDT-Vallex, EngVallex and with examples from the PCEDT.
Description:
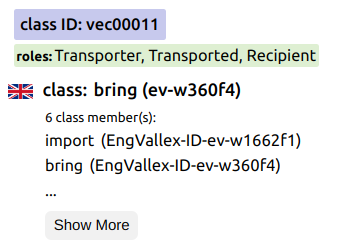
SynSemClass lexikon version 5.1 explores the contextual semantic "equivalence" of Czech, English, German, and Spanish verbs, together with their valence behaviour in parallel Czech-English, German-English, and Spanish-English texts. SynSemClass5.1 is an ontology based on classes of multilingual verb synonyms, supplemented by semantic roles. The SynSemClass event-type ontology is enriched by a considerable number of new classes and the inclusion of Spanish synonyms is a novelty compared to older versions. Again, it contains references to other semantic lexical sources. In addition to the references already used (to PDT-Vallex, EngVallex, CzEngVallex, FrameNet, VerbNet, PropBank, Ontonotes Woxikon, E-VALBU, GUP, and German FrameNet), SynSemClass also includes references to Spanish linguistic lexical resources: to ADESSE, SenSem, AnCora, and Spanish WordNet and FrameNet. Examples of sentences in which multilingual synonyms have been used are also included.
Description:
The SynSemClass Search Tool is a web-based interface designed for querying the SynSemClass ontology (version 4.0 and higher), an event-type ontology available in multiple languages. It includes several search options and criteria for building complex queries. The search results are presented in a clear and user-friendly interactive format. Additionally, the tool offers an API, allowing users to retrieve either the search results identical to the UI, or the raw server response for further processing.
Description:
The ILRB has been created by two cooperating teams - by the team of the Institute of Czech Language, Czech Academy of Sciences and the team of the NLP Centre at the Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University (2004-2008).
The tool consists of two sections: wordlist and reference (explanatory) one. Comments and remarks are welcome and should be send to the address poradna@ujc.cas.cz.
1. Wordlist section
It contains more than 60 000 dictionary entries and is based on the glossary of the School Rules of Czech Orthography, the Dictionary of the Literary Czech and selected entries from the New Dictionary of Words of Foreign Origin and Dictionary of Neologisms. The entries typically include information that is asked about frequently by the users. Also inflectional forms of the particular words forms are offered in the form of tables thanks to the morphological analyzer ajka created at the Faculty of Informatics, MU. The dictionary part is linked to the explanatory one through the hypertext links.
2. Reference section
It comprises the explanations about linguistic phenomena described in the Rules of Czech Orthography and contemporary Czech grammars, frequently and repeatedly asked by the users turning to the Linguistic Advisory Line in the Institute of Czech Language. In the offered explanations some typical spelling problems are dealt with including the appropriate recommendations. The ILRB is regularly updated and completed, new expressions are added and made more precise.
Description:
ElixirFM is a high-level implementation of Functional Arabic Morphology. ElixirFM can process words of Modern Written Arabic using four different modes. Here, you can learn how to use these modes for various purposes.
Description:
The Dialogy.Org system allows users to search texts (transcripts), watch video recordings and view F0 acoustic wave forms. The Dialogy.Org system works on the principle of web-based interface, so installation of additional programs on your computer is not necessary. You must have Flash Player for playing video recordings.
Description:
Korektor is a statistical spell- and (occasional) grammar-checker. This spellchecker strarted with Michal Richter's diploma thesis Advanced Czech Spellchecker, but it is being developed further. There are two versions: a unix command line utility (tested on Debian, Ubuntu and OS X) and an OS X SpellServer with a System Service, that integrates with native OS X GUI applications.
Description:
KonText is a basic web application for querying corpora available within the LINDAT/CLARIN project. It allows evaluation of simple and complex queries, displaying their results as concordance lines, computing frequency distribution, calculating association measures for collocations and further work with language data. This instance is a fork of KonText application (developed by the Institute of the Czech National Corpus) that has been further extended by the Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics to suit the needs of LINDAT/CLARIN project.
Description:
KER is a keyword extractor that was designed for scanned texts in Czech and English. It is based on the standard tf-idf algorithm with the idf tables trained on texts from Wikipedia. To deal with the data sparsity, texts are preprocessed by Morphodita: morphological dictionary and tagger.
Description:
EVALD 4.0 serves for automatic evaluation of surface coherence (cohesion) in Czech texts written by native speakers of Czech.
Description:
EVALD 4.0 for Foreigners is a software for automatic evaluation of surface coherence (cohesion) in Czech texts written by non-native speakers of Czech.
Description:
EVALD 4.0 for Beginners is a software for automatic evaluation of surface coherence (cohesion) in Czech texts written by non-native speakers of Czech - language beginners.
Description:
UWebASR is a user-friendly Web-based ASR engine for Czech and Slovak that is free to use for research purposes and does not require any background knowledge about the inner workings of the ASR engine or the API usage. The uploaded audio recording is automatically transcribed and stored in a structured XML format that allows efficient manual post-processing.
Description:
TEITOK is an online platform for searching, visualising, and managing linguistic corpora, in which corpus files are kept in the rich TEI/XML file format. At LINDAT, TEITOK is integrated with Kontext and PML-TQ that allows access to the same corpus from a range of different interfaces.